Glutathione
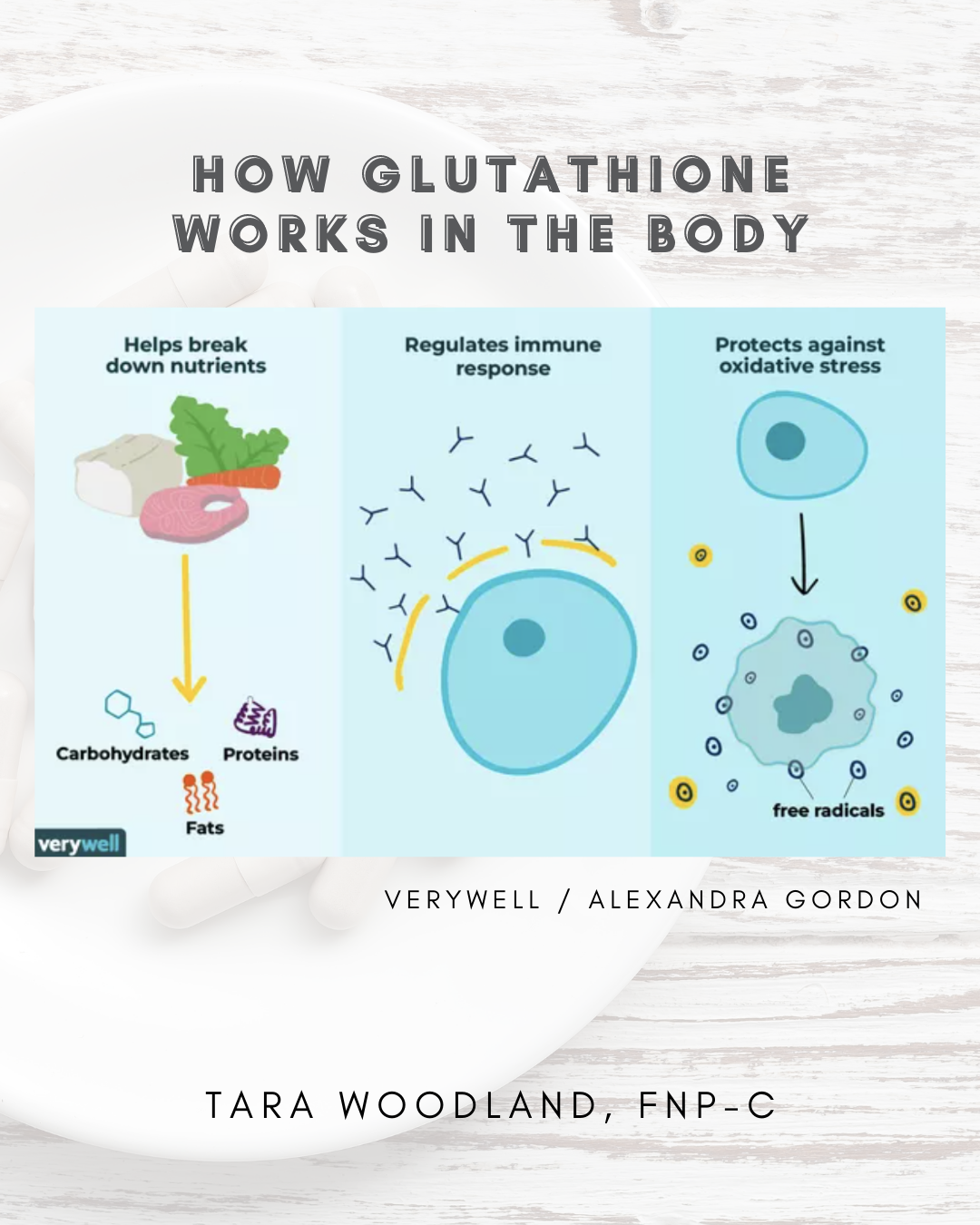
Glutathione is a tripeptide made of 3 amino acids, glutamine, glycine, and cysteine. It is produced by the liver and nerve cells in the central nervous system. It is a powerful free radical and reactive oxygen species scavenger, and plays an important role in the immune system. Free radicals are unstable molecules that form in response to various factors such as the environment and diet. When an imbalance occurs and there are more free radicals than antioxidants, oxidative cell damage occurs and this can lead to inflammation.
There is one study that supports it may be helpful in Covid-19 as well; “antioxidants like Glutathione and its precursor, N-acteylcysteine (NAC) have been considered in treatment of this condition given their influence on binding of the viral protein on to the host cell ACE2 receptor protein that is specifically implicated in the SARS-Cov-2 infection.” 3
Several things can lower glutathione levels, environmental toxins, stress, poor diet, poor sleep, and aging. It is naturally produced in the body, but can also be taken orally, intravenously, and by nebulization.
Low glutathione levels may play a role in neurodegenerative diseases, pulmonary diseases, liver diseases, immune disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and the aging process. There is a study showing those with autism may have higher levels of oxidative stress which in turn lowers glutathione levels.
“The state of oxidative stress is defined as an imbalance between the presence of antioxidants and free radicals/pro-oxidants in a biological system. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are the two most common residual products of various cellular processes, including aerobic metabolism [37]. When the redox balance is disrupted, excessive production of free-radicals start to cause significant damage as the body is left unable to counteract the overproduction of these oxidant agents. The unstable atoms in free-radicals take away electrons from other biological structures, causing instability and damage to cells and essential components such as DNA, proteins and lipids from the membrane, which ultimately lead to inflammation tissue injury[38].” 3
It is believed that taking glutathione orally isn’t the best route due to an intestinal enzyme, γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT), which degrades glutathione. Glutathione production relies on N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and taking this orally may help raise glutathione levels. Due to the poor absorption orally, it may be better to take glutathione sublingually, intravenously, or by nebulization. Topically can also be a great option for absorption.
Personally I have been nebulizing glutathione and loving how easy and affordable it is. I don’t mind the sulfa (egg) smell and it diminishes quickly.
** If you are getting a covid vaccine this is an important tool before and after to help the immune system be as primed as possible. Same for unvaccinated, too!
Product Options
For Nebulizing
In general you want 1/8 tsp glutathione with 7-10ml sterile saline
Sterile Saline or make your own
1 cup of water (boil water for 20 minutes)
1/2 tsp of salt (do not use sea salt)
wash the hands thoroughly
sterilize the container and mixing utensil by using a dishwasher or boiling them in water
pour the water into the container
mix in the salt and stir until completely dissolved
let the mixture cool before use
Store in fridge
Bulk Supplements Reduced Glutathione (can also grab on Amazon)
TheraNaturals Reduced L-Glutathione Plus
How to prepare:
Mix it when you need it so it’s always fresh. Break capsule/s open and empty the content into a container/cup. Add 3 ml (~1/2 tsp) pure saline solution to the container/cup. Let agitate briefly until the solution is clear. It’s now ready to use.
Water to capsule ratio:
1-3 capsules: 3 ml saline
4 capsules: 4 ml saline
5 capsules: 5 ml saline
6 capsules: 6 ml saline
Oral
Liposomal Glutathione - Pure Encapsulations (Fullscript)
Liposomal Glutathione -Designs for Health (Fullscript)
Topical
Oxicell® or Oxicell-SE (without essential oils) - Apex Energetics, Inc (Fullscript)
These options have other ingredients and not just glutathione
References
Lana JFSD, Lana AVSD, Rodrigues QS, Santos GS, Navani R, Navani A, da Fonseca LF, Azzini GOM, Setti T, Mosaner T, Simplicio CL, Setti TM. Nebulization of glutathione and N-Acetylcysteine as an adjuvant therapy for COVID-19 onset. Adv Redox Res. 2021 Dec;3:100015. doi: 10.1016/j.arres.2021.100015. Epub 2021 Aug 8. PMID: 35425932; PMCID: PMC8349474.
Schmitt B, Vicenzi M, Garrel C, Denis FM. Effects of N-acetylcysteine, oral glutathione (GSH) and a novel sublingual form of GSH on oxidative stress markers: A comparative crossover study. Redox Biol. 2015 Dec;6:198-205. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.07.012. Epub 2015 Jul 29. PMID: 26262996; PMCID: PMC4536296.
Lana JFSD, Lana AVSD, Rodrigues QS, Santos GS, Navani R, Navani A, da Fonseca LF, Azzini GOM, Setti T, Mosaner T, Simplicio CL, Setti TM. Nebulization of glutathione and N-Acetylcysteine as an adjuvant therapy for COVID-19 onset. Adv Redox Res. 2021 Dec;3:100015. doi: 10.1016/j.arres.2021.100015. Epub 2021 Aug 8. PMID: 35425932; PMCID: PMC8349474.
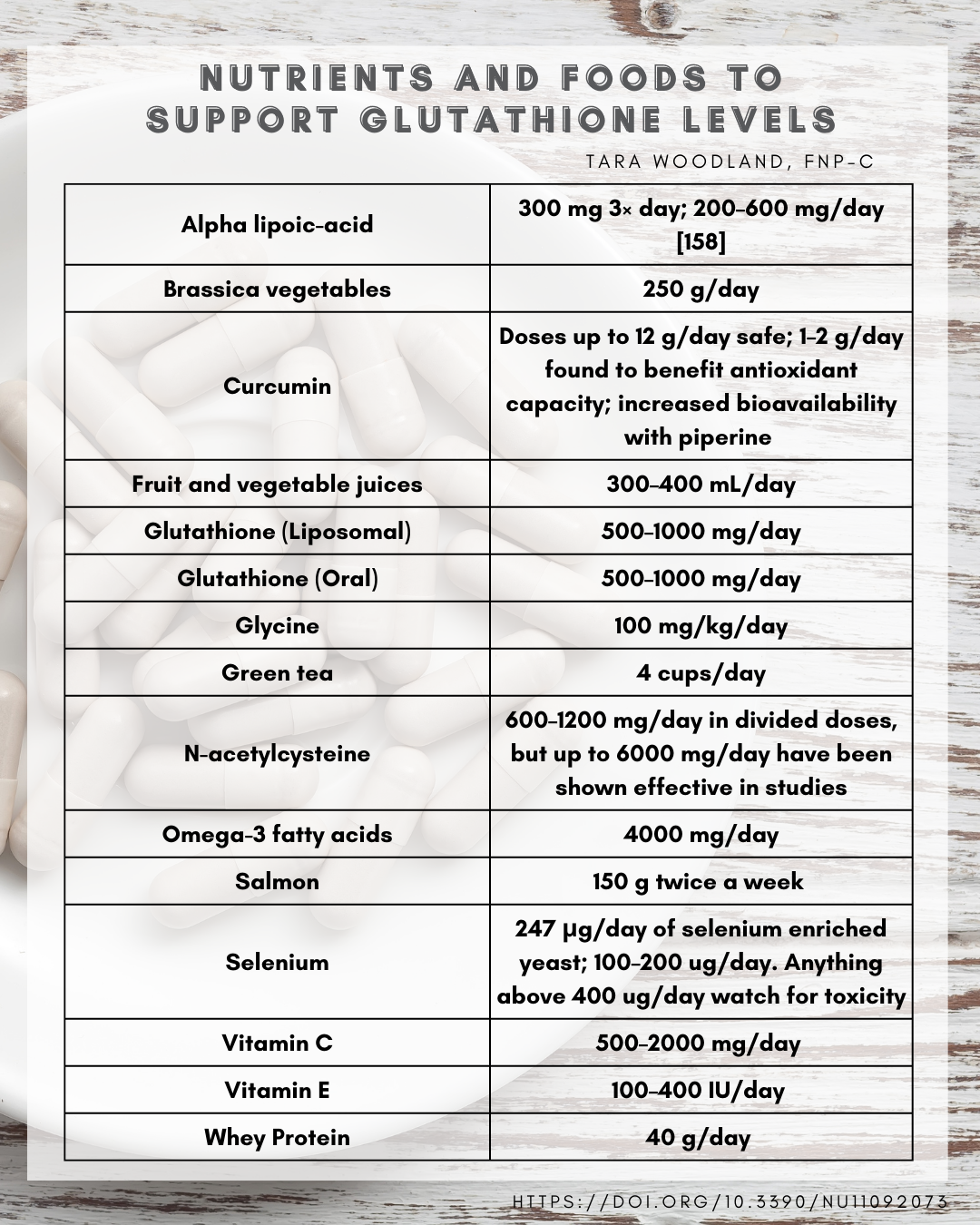
Minich DM, Brown BI. A Review of Dietary (Phyto)Nutrients for Glutathione Support. Nutrients. 2019; 11(9):2073. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11092073
https://www.verywellhealth.com/benefits-of-glutathione-89457
Forman HJ, Zhang H, Rinna A. Glutathione: overview of its protective roles, measurement, and biosynthesis. Mol Aspects Med. 2009 Feb-Apr;30(1-2):1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2008.08.006. Epub 2008 Aug 30. PMID: 18796312; PMCID: PMC2696075.